Objectives:
Identify the anatomical structures, indications, and contraindications of hair transplantation.
Describe the instrumentality, personnel, preparation, and technique with regard to hair transplantation.
Review the acceptable analysis of the potential complications and clinical significance of hair transplantation.
Summarize interprofessional team methods for rising care coordination and communication to advance hair transplantation and improve outcomes.
Access free multiple alternative queries on this subject.
Go to:
Introduction
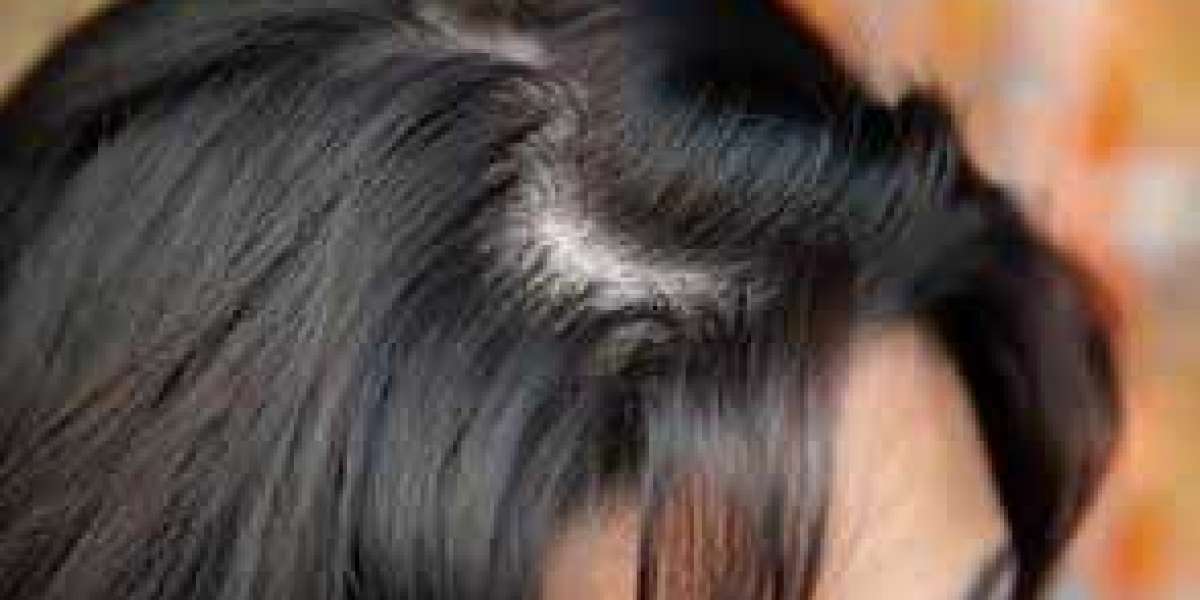
Hair loss represents a distressing issue poignant an outsized portion of the population, together with up to eighty fifth of males and four-hundredth of females, and its incidence will increase with age for each sexes. although several causes of hair loss exist, out and away the foremost common etiology is steroid baldness (AGA), associate degree androgen-sensitive pattern of hair loss that affects each men and ladies.[1] Indeed, non-surgical modalities exist which can halt the progression of steroid baldness and even facilitate grow new hairs (i.e., minoxidil, finasteride, dutasteride, low-level optical maser lightweight medical aid, platelet-rich plasma, adenosine, ketoconazole) [2][3] even so, recent advancements in surgical hair restoration have created hair transplantation (HT) associate degree progressively effective, safe, and reliable approach for patients distressed by steroid baldness to regain a younger and natural look of their hair.[4]
Go to:
Anatomy and Physiology
It is essential to grasp the relevant anatomy and physiology of hair, and also the hair cycle, so as to maximise the outcomes of hair transplantation at Hair Transplant in Abu Dhabi. Key parts in hair restoration include[5]:
Hair follicle – composed of a hair shaft, 2 encompassing sheaths (inner and outer), and a germinative bulb. The vesicle divides into 3 sections: body structure (from the skin surface to the sebaceous follicle duct), the isthmus (from the fatty duct to the arrector pili muscle insertion), and also the inferior phase (from the muscle insertion to the bottom of the matrix)
Bulb – the deepest phase of the follicle that contains the hair matrix (creates the hair shaft), dermal papilla (regulates growth), and melanocytes (produce color).
Terminal hair – thick, pigmented hairs at the highest of the scalp, beard, axillary, and bone regions, all of that square measure androgen-sensitive. The hair elsewhere on the body, together with the membrane bone and bone scalp, square measure androgen-independent.
Vellus hair – this can be fine, short, non-pigmented hairs ("peach fuzz") found on the adult that covers a lot of of the body.
Follicular Unit (FU) – a present cluster of hair(s) seen on the scalp consisting of many terminal hairs (usually one to 4), a sebaceous follicle and duct, associate degreed an arrector pili muscle. The scleroprotein band that surrounds the FU is termed the perifolliculum.
Scalp Hair Growth Cycle [6]
Anagen – the 2- to 6-year active growing part of the follicle. around ninety to ninety fifth of scalp hairs square measure in anagen at any given time.
Catagen – this can be the 2- to 3-week involutional part of the follicle characterised by acute vesicle regression. but I Chronicles of scalp hairs square measure in catagen at any given time.
Telogen – the 2- to 3-month resting part of the follicle characterised by a stop altogether activity. around five to 100% of scalp hairs square measure in telogen at any given time.
Exogen – the daily shedding part of the follicle characterised by a loss of twenty five to a hundred telogen hairs, that square measure replaced by new anagen hairs.